What is an IP Address?
An IP address (Internet Protocol address) is a unique identifier for a device on a network. It’s like your home address but for computers.
Types of IP Addresses:
- IPv4 (e.g.,
192.168.1.1) – Most common, but limited. - IPv6 (e.g.,
2001:0db8:85a3::8a2e:0370:7334) – Newer, more addresses available.
Public vs. Private IP:
- Public IP – Unique on the internet (e.g., Google’s
8.8.8.8). - Private IP – Used within a local network (e.g.,
192.168.1.1for your router).
Hands-On Task: Find Your IP Address
Try these commands on your terminal:
Find your public IP (internet IP):
curl ifconfig.meor
curl icanhazip.comFind your private IP (local network IP):
On Linux/macOS:
ip aOn Windows (Command Prompt):
ip config
Subnetting (Breaking Down Networks)
What is Subnetting?
Subnetting is dividing a large network into smaller, more manageable networks (subnets). This helps with:
✅ Efficient IP allocation
✅ Better security
✅ Reduced network congestion
IP Address Structure (IPv4)
An IPv4 address has four numbers (octets) separated by dots, each ranging from 0 to 255. Example
Each IP address consists of two parts:
- Network Portion – Identifies the network
- Host Portion – Identifies a specific device
The Subnet Mask tells us how many bits belong to the network and how many belong to hosts.
Understanding Subnet Masks
A subnet mask determines which part of an IP address belongs to the network and which part is for devices.
Common subnet masks:
| Subnet Mask | CIDR Notation | Usable IPs |
|---|---|---|
| 255.0.0.0 | /8 | 16,777,214 |
| 255.255.0.0 | /16 | 65,534 |
| 255.255.255.0 | /24 | 254 |
| 255.255.255.128 | /25 | 126 |
Example:
- IP Address:
192.168.1.10 - Subnet Mask:
255.255.255.0(/24)- Network Portion:
192.168.1 - Host Portion:
10 - Usable IPs: 254 (from
.1to.254)
- Network Portion:
Hands-on Task: Check Your Subnet Mask
On macOS, run:
ifconfig | grep netmask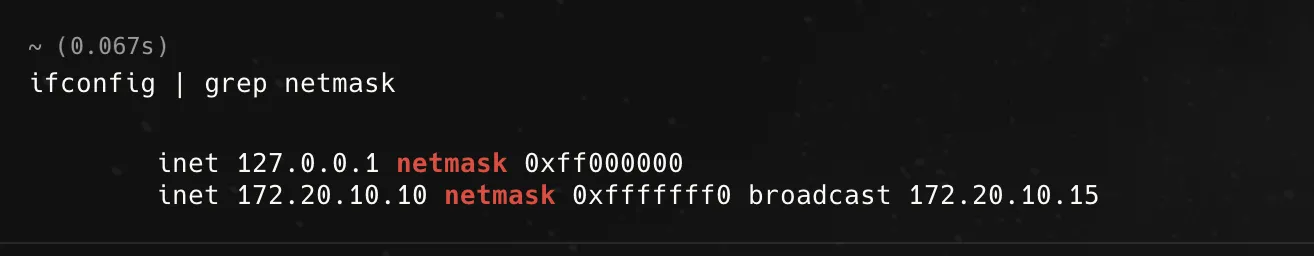
Understanding the Output
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 0xff000000
- This is the loopback address (
127.0.0.1). - It’s used for internal communication within your device (your computer talking to itself).
- The netmask
0xff000000(hexadecimal) is equivalent to 255.0.0.0 or /8 in CIDR notation.
inet 172.20.10.10 netmask 0xfffffff0 broadcast 172.20.10.15
- This is your actual private IP address (
172.20.10.10). - It belongs to the 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255 range, which is for private networks.
- Netmask:
0xfffffff0(hex) = 255.255.255.240 (CIDR: /28)- This means your network has 16 total IPs (14 usable: .1 to .14, since .0 is the network and .15 is the broadcast).
What This Means for Your Network
- You are on a private network with a small subnet (/28).
- Your network can support up to 14 devices (IP range:
172.20.10.1to172.20.10.14). - The broadcast address (
172.20.10.15) is used to send messages to all devices on this subnet.
Next Steps: Practice Subnetting
Try answering these questions:
- If you had a /24 subnet mask (255.255.255.0) instead of /28, how many usable IPs would you have?
- Convert 255.255.255.192 into CIDR notation and tell me how many usable IPs it provides.
TERMINOLOGY TO KNOW
What is a Loopback Address?
Loopback address = 127.0.0.1
What does it do?
It lets your computer talk to itself.
Why is that useful?
- Testing if your network stack is working.
- Running servers or services locally without internet.
- Developers use it all the time.
Think of 127.0.0.1 like calling your own phone number—it rings, and you’re the one answering.
What is a Broadcast Address?
It’s a special IP used to send data to every device on the subnet.
Why is it needed?
Let’s say you want to alert every device connected to your network (“hey everyone, please refresh your DNS settings!”) — you send that message to the broadcast address. Everyone on the subnet hears it.
So in /28, broadcast = 172.20.10.15
